How to Live a Fulfilling Life with Psoriasis?
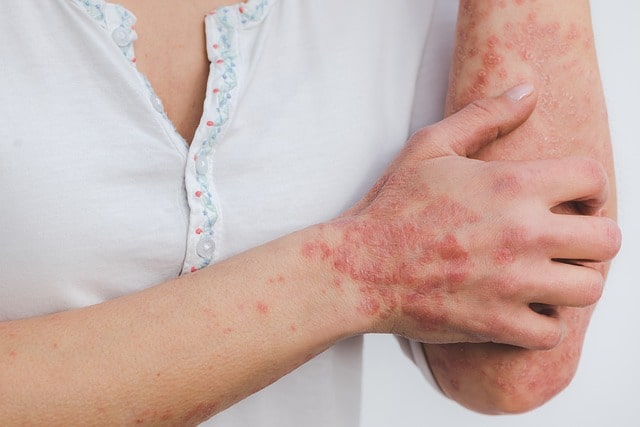
Psoriasis is not just a skin problem. It is a condition that cannot be compared to other skin disorders because it has an autoimmune nature. Normally, healthy skin cells renew about once a month, but in psoriasis, skin cells rise too quickly and accumulate on top of each other.
According to individuals living with psoriasis, their quality of life is comparable to those suffering from diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular diseases. These individuals often feel isolated and believe that nobody understands them. In stressful situations, they may experience intense itching of the skin.
Even choosing clothing is related to minimizing irritation on the skin and ensuring that the shedding scales are not visible. When sitting on a seat with dark upholstery, these individuals feel embarrassed by the layer of white scales left behind on the seat. This condition affects all aspects of life, and the social aspect, particularly personal relationships, often suffers the most.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The most common symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Red patches of skin that can be silvery or white in appearance;
- Affected skin that can be sensitive, itchy, and painful;
- Scaling of the skin;
- Cracked skin that easily bleeds;
- Changes in the colour and texture of nails, including nail fungus;
- Nails that separate from the nail bed may be painful or bleed;
- Emotional problems and depression due to skin issues.
Some statistics.
Approximately 1 million Canadians have been diagnosed with psoriasis. This condition occurs equally among men and women and can onset at any age, although it is more commonly seen in adults.
Types of psoriasis
This condition has several forms, and psoriasis can affect:
- The skin, which is the most commonly affected area.
- Joints, with approximately 30% of psoriasis patients experiencing arthritis.
- Nails. Up to 80% of individuals with psoriasis have nail problems, and 10% of them exclusively have nail issues.
- Scalp affects up to 50% of psoriasis patients.
- Genitalia, which are affected in over 60% of individuals with psoriasis at least once during their lifetime.
- Occasionally, psoriasis may appear on the lips.
Psoriasis triggers
Psoriasis Triggers Psoriasis can go into remission for a certain period and then flare up again due to specific factors. There are several triggers that can exacerbate psoriasis:
- Infections, such as upper respiratory tract bacterial or viral infections, can trigger the development or exacerbation of psoriasis.
- Skin injuries or any areas of skin trauma can cause the spread of psoriasis or the emergence of new lesions. These injuries can include cuts, burns from shaving, insect bites, cuts, scrapes, sunburns, needle pricks, or bruises.
- Medications such as lithium, beta-blockers, and antimalarial drugs can predispose individuals to psoriasis flare-ups or initial onset.
- Stress can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
- The dry and cold winter season seems to have an adverse effect on psoriasis, as it dries out and irritates the skin.
- Smoking, alcohol consumption, and obesity increase the risk of developing psoriasis and its severity.
Various Complications Associated with Psoriasis
Psoriasis increases the risks of various diseases, including:
- Cancer
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Crohn’s disease
- Depression
- Diabetes
- Metabolic syndrome
- Obesity and osteoporosis, which can result from inadequate physical activity
- Uveitis (inflammatory eye disease)
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Causes of psoriasis
Most doctors are unsure about the exact cause of psoriasis, but there are several associated factors that can trigger psoriasis in individuals with a genetic predisposition. These factors include:
- Autoimmunity tendencies;
- Poor nutrition;
- Elevated levels of T-cells;
- Severe emotional stress;
- Hormonal changes, estrogen dominance;
- Genetics;
- Vitamin D deficiency;
- Impaired liver function;
- High levels of environmental toxins;
- Leaky gut syndrome.
Psoriasis and Leaky Gut Syndrome
Psoriasis is closely linked to leaky gut syndrome, and treating this condition often improves the overall psoriasis condition. It’s worth noting that addressing a leaky gut can improve many autoimmune issues. This connection arises from undigested food particles entering the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and potentially leading to an autoimmune response when the immune system starts attacking these particles, which have a similar structure to certain tissues in our bodies.
After decades of research, a strong correlation has been found between gut health and skin health. Experts believe that the body may attempt to eliminate toxins through the skin, leading to psoriasis symptoms.
Traditional treatment
Since psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, treatment methods primarily focus on suppressing the excessive immune response. Medications may be changed if they are not effective or stop working.
Currently, the most common treatments include retinoids or immunosuppressants (such as steroids or cyclosporines). However, these medications can have side effects even if they are effective in treating psoriasis.
Alternative Treatments
Alternative Treatment Methods There are several methods that can be used to manage psoriasis without side effects. Here are a few of them, taking into account the language used in Canada:
- Stress reduction.
- Physical activity.
- Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
- Take baths with Epsom salt, but avoid using water that is too hot. Do not stay in the water for more than 15 minutes; this is enough time to remove dead scales.
- After bathing, apply moisturizing creams such as aloe or emu oil. There are also several creams that have proven to be effective in treating psoriasis. They contain avocado oil, vitamin B12, vitamin D, and vitamin A.
- Vitamin D deficiency often worsens the skin condition in individuals with psoriasis.
- Supplements that improve skin condition can be used, such as antioxidants and Omega-3, for example.
- Follow an anti-inflammatory diet for psoriasis.
- Local cryotherapy can help reduce inflammation and accelerate the healing of affected tissues.
- Low Dose Naltrexone (LDN) can help reduce inflammation and alleviate itching. This medication is beneficial for almost all autoimmune conditions.
Conclusion
Psoriasis is an autoimmune problem. This means that anything that improves the functioning of the immune system will also alleviate psoriasis symptoms.
It may seem strange, but diet is actually the most effective approach when it comes to treating psoriasis.
